Many in member countries express reservations about fulfilling Article 5’s collective defense obligations
By and February 9, 2020
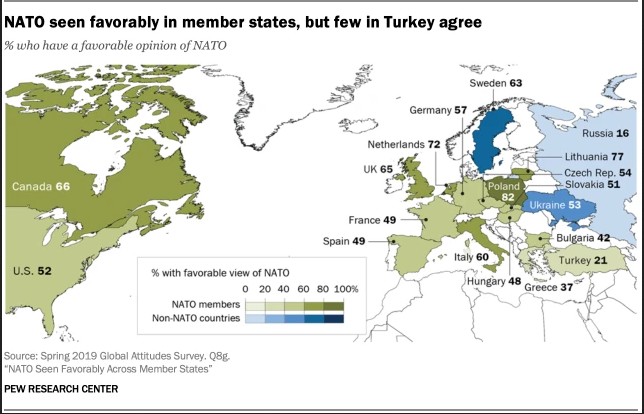
NATO is generally seen in a positive light across publics within the alliance, despite lingering tensions between the leaders of individual member countries. A median of 53% across 16 member countries surveyed have a favorable view of the organization, with only 27% expressing a negative view. But opinions of NATO and related issues vary widely across the countries surveyed, especially regarding the obligations of Article 5 of the 70-year-old Washington Treaty, which declares that an attack against one member nation is considered an attack against all members.
Positive ratings of NATO among members range from a high of 82% in Poland to 21% in Turkey, with the United States and Germany in the middle at 52% and 57%, respectively. And in the three nonmember states surveyed, Sweden and Ukraine see the alliance positively (63% and 53%, respectively), but only 16% of Russians say the same.
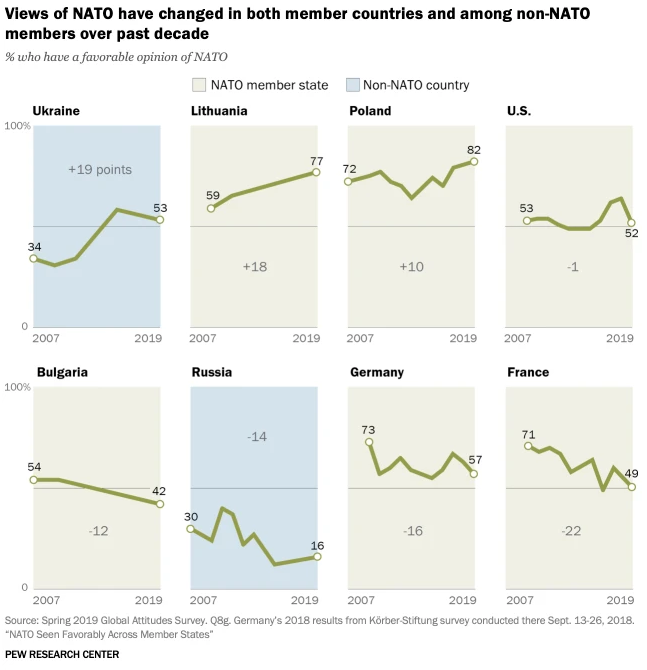
Favorable views of the organization have fluctuated over time among both NATO member and nonmember countries. Since the late 2000s, favorable opinions of NATO are up 10 percentage points or more in Ukraine, Lithuania and Poland. However, positive opinions of NATO are down significantly in Bulgaria, Russia, Germany and France over the past decade, with double-digit percentage point declines in each of these countries. Favorable views of the organization are also down significantly in Spain and the Czech Republic.
In addition, across several countries surveyed, favorable views of the organization are related to ideological orientation, with those on the right sharing a more positive view than those on the ideological left.
 NATO serves as a political and military alliance for its 29 member states spanning Europe and North America. Founded in 1949 to provide collective defense against the Soviet Union, the alliance seeks to balance Russian power and influence, in addition to a host of other operations.
NATO serves as a political and military alliance for its 29 member states spanning Europe and North America. Founded in 1949 to provide collective defense against the Soviet Union, the alliance seeks to balance Russian power and influence, in addition to a host of other operations.
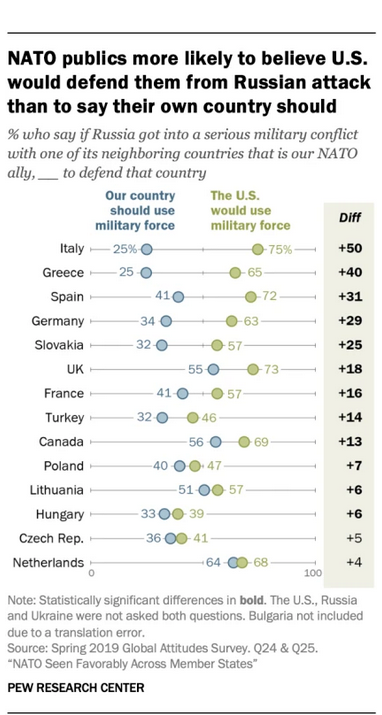
Despite the organization’s largely favorable ratings among member states, there is widespread reluctance to fulfill the collective defense commitment outlined in Article 5 of NATO’s founding treaty. When asked if their country should defend a fellow NATO ally against a potential attack from Russia, a median of 50% across 16 NATO member states say their country should not defend an ally, compared with 38% who say their country should defend an ally against a Russian attack.
Publics are more convinced that the U.S. would use military force to defend a NATO ally from Russia. A median of 60% say the U.S. would defend an ally against Russia, while just 29% say the U.S. would not do so. And in most NATO member countries surveyed, publics are more likely to say the U.S. would defend a NATO ally from a Russian attack than say their own country should do the same.
In terms of transatlantic relations, some Western European publics prefer a close relationship with the U.S., but many others prefer a close relationship with both the U.S. and Russia. Nevertheless, few want to prioritize their relationship with Russia over their U.S. relations. Ideology also relates to views of potential allies: Those on the right in several countries are more likely than those on the left to prefer a relationship with the U.S.
Despite the reservations many have about NATO’s Article 5 commitments, half or more in nearly every country surveyed agree it is sometimes necessary to use military force to maintain order in the world. In most countries surveyed, those who say military force is sometimes necessary are also more likely to agree that their country should use military force to defend a fellow NATO ally.
These views have changed significantly over the past decade in some countries. In Ukraine, Russia, Slovakia and Germany, more say military force is sometimes necessary than said the same in 2007. And in Italy, Spain and the Czech Republic, publics have grown less inclined to agree.
On the topic of territorial ambitions, when asked if there are parts of neighboring countries that really belong to their country, relatively few surveyed agree. However, among NATO member states, majorities in Hungary, Greece, Turkey and Bulgaria agree that parts of other countries belong to them. In many European countries, those with a favorable view of right-wing populist parties are more likely to support this statement.
These are among the key findings from a Pew Research Center survey of 19 countries, including 16 NATO member states, Sweden, Russia and Ukraine. The survey was conducted among 21,029 people from May 13 to Aug. 12, 2019. Throughout this report, German results are occasionally sourced from a series of surveys conducted in Germany by Körber-Stiftung, in partnership with Pew Research Center.
Read more at https://www.pewresearch.org/global/2020/02/09/nato-seen-favorably-across-member-states/