Lamya Khalidi
Published online: 16 October 2017
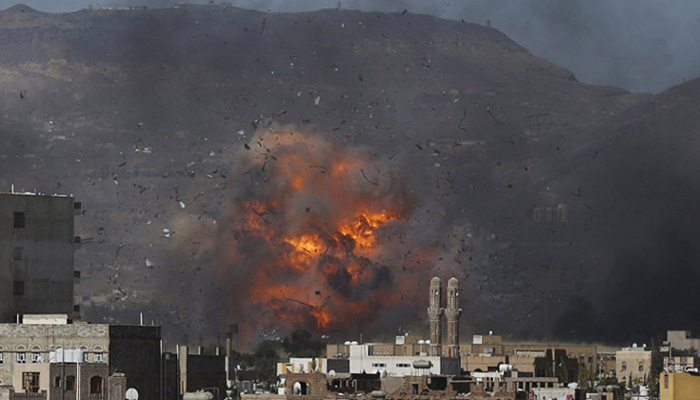
After losing control of the capital Sanaa to Yemen’s northern Houthi movement, which is aligned with forces loyal to the former president ʿAli ʿAbd Allah Salih, current Yemeni President ʿAbd Rabbu Mansur Hadi turned to Saudi Arabia for help. In March 2015, Saudi Arabia and its coalition of nine states began a bombing campaign in Yemen, the poorest country in the Arab world. Prior to the conflict, Yemen was already 90-percent dependent on imported food and had been battling a severe water deficit. A twenty-eight-month-long siege of its civilian population has left the country in a situation that some humanitarian groups deem to be worse than the crisis in Syria. The media has barely covered Yemen’s catastrophic crisis, partially because of overt censorship by the Saudi kingdom and a shielding of its systemic violations of international law by powerful allies including the United States, the United Kingdom, and France. These countries are clearly more concerned with billion-dollar arms deals with the kingdom than with putting an end to what has been described as the worst food crisis since the establishment of the United Nations.
Published in https://www.cambridge.org