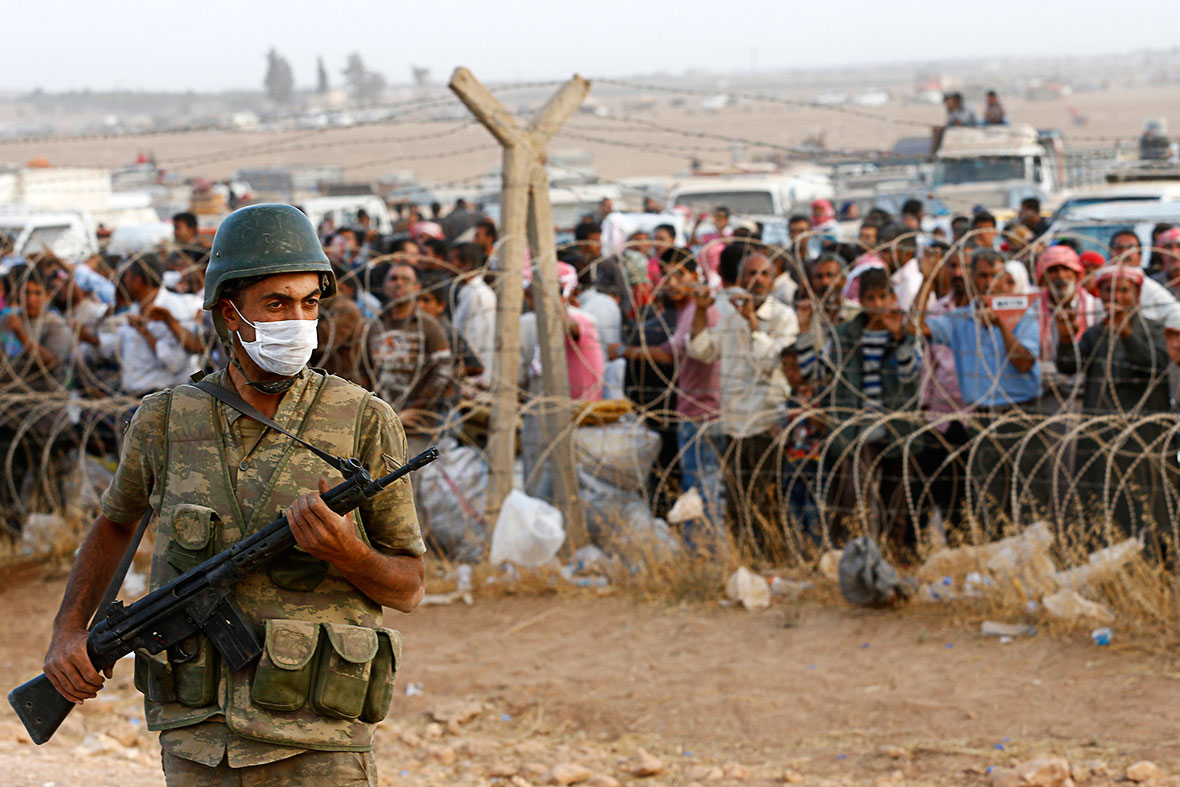
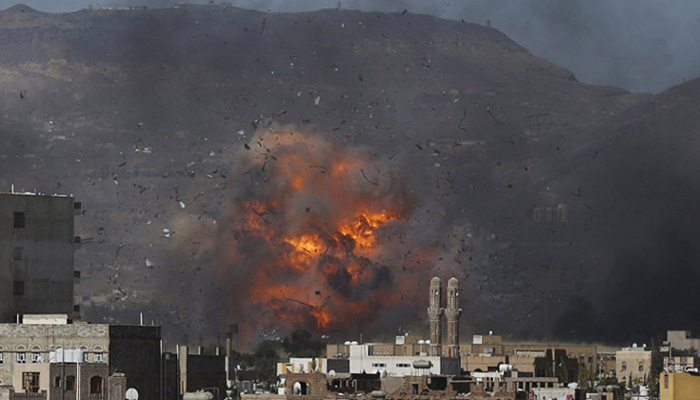
On the eve of President Obama’s April 2016 visit to Saudi Arabia, the U.S. Congress began debating the Justice Against Sponsors of Terrorism Act (JASTA), that would, inter alia, allow the families of victims of the September 11 attacks to sue the Saudi government for damages. Also in April 2016, the New York Times published that a 2002 congressional inquiry into the 9/11 attacks had found that Saudi officials living in the United States at the time had a hand in the plot. The commission’s conclusions, said the paper, were specified in a report that has not been released publicly.[1]
The JASTA bill, which was passed by the Senate on May 17, 2016, triggered fury in Saudi Arabia, expressed both in statements by the Saudi foreign minister and in scathing attacks on the U.S. in the Saudi press.[2] On April 28, 2016, the London-based Saudi daily Al-Hayat published an exceptionally harsh article on this topic by Saudi legal expert Katib Al-Shammari, who argued that the U.S. itself had planned and carried out 9/11, while placing the blame on a shifting series of others – first Al-Qaeda and the Taliban, then Saddam Hussein’s regime in Iraq, and now Saudi Arabia. He wrote that American threats to reveal documents that supposedly point to Saudi involvement in 9/11 are part of standard U.S. policy of exposing archival documents to use as leverage against various countries – which he calls “victory by means of archives.”
Following are excerpts from Al-Shammari’s article:[3]
“Those who follow American policy see that it is built upon the principle of advance planning and future probabilities. This is because it occasionally presents a certain topic to a country that it does not wish [to bring up] at that time but [that it is] reserving in its archives as an ace to play [at a later date] in order to pressure that country. Anyone revisiting… [statements by] George H.W. Bush regarding Operation Desert Storm might find that he acknowledged that the U.S. Army could have invaded Iraq in the 1990s, but that [the Americans] had preferred to keep Saddam Hussein around as a bargaining chip for [use against] other Gulf states. However, once the Shi’ite wave began to advance, the Americans wanted to get rid of Saddam Hussein, since they no longer saw him as an ace up their sleeve.
Read the full article here: